DAO Governance Tokens: Empowering Decentralized Decision-Making
Exploring the Role of Governance Tokens in Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have emerged as a groundbreaking concept, revolutionizing the way communities make decisions and govern their operations. At the heart of DAOs lies the power of governance tokens, which enable token holders to actively participate in shaping the future of these autonomous entities. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of DAO, the governance tokens of DAO, exploring their role in decentralized governance, the mechanisms they employ, and the transformative potential they hold. Join us as we unlock the intricacies of DAO governance tokens and discover how they empower decentralized decision-making in the ever-evolving landscape of blockchain technology.
The Advent of DAO:

Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has rapidly gained popularity and disrupted traditional financial systems by offering open, permissionless, and transparent financial services on the blockchain. One of the most significant developments within the DeFi space has been the emergence of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).DAOs are groundbreaking entities that operate without the need for a centralized authority, allowing for decentralized decision-making and community governance.
DAOs are built on blockchain networks, primarily Ethereum, and are governed by smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and enables stakeholders to participate in decision-making processes by holding governance tokens.
The advent of DAOs has had a profound impact on the DeFi industry in several ways. Firstly, DAOs have revolutionized fundraising through Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Initial DEX Offerings (IDOs). In traditional fundraising models, startups and projects typically rely on venture capitalists or angel investors for funding. However, DAOs allow for decentralized crowdfunding, where individuals can contribute funds to a project in exchange for governance tokens. This democratizes the investment process, allowing ordinary users to become stakeholders and actively participate in decision-making.
DAO Tokens: Your vote matters
DAO governance tokens are cryptographic tokens that serve as a crucial component of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). These tokens represent ownership rights and voting power within the organization, enabling token holders to participate in key decision-making processes. Unlike traditional centralized organizations where decision-making is concentrated in the hands of a few individuals or entities, DAO governance tokens distribute power and authority among a community of token holders, fostering a more inclusive and decentralized governance model.
Functionality and Features:

DAO governance tokens possess several key features and functions that contribute to their significance in decentralized decision-making:
a) Voting Rights: One of the primary functions of DAO governance tokens is to grant holders the right to vote on proposals and decisions within the DAO ecosystem. Each token typically represents a specific voting weight, allowing token holders to influence the outcome of governance decisions based on their token holdings.
b) Proposal Submission: Governance token holders often have the privilege to submit proposals for consideration by the DAO community. These proposals can range from protocol upgrades, parameter adjustments, funding requests, to changes in organizational structure. The ability to propose and shape the direction of the organization gives token holders an active role in decision-making.
c) Staking and Delegation: DAO governance tokens can be staked to earn additional rewards or to delegate voting power to trusted individuals or entities. Staking incentivizes token holders to actively participate in the governance process by providing them with additional economic benefits. Delegation allows token holders to entrust their voting rights to representatives, who can vote on their behalf.
d) Rewards and Incentives: DAOs often distribute rewards and incentives to governance token holders as a way to incentivize their active involvement in the governance process. These rewards can come in the form of additional tokens, protocol fees, or other benefits tied to the DAO ecosystem. By aligning the interests of token holders with the success of the organization, DAO governance tokens promote community engagement.
e) Token Locking and Vesting: To encourage long-term commitment and prevent token manipulation, some DAO governance tokens may include mechanisms such as lock-up periods and vesting schedules. These features ensure that token holders are invested in the DAO's success over the long term, reducing the potential for short-term speculation and increasing the stability of decision-making processes.
f) Governance Upgradability: DAO governance tokens often come with the flexibility to upgrade and evolve the governance mechanisms over time. This allows DAOs to adapt to changing needs and incorporate improvements based on the feedback and consensus of the community. Upgradability ensures that the governance framework remains dynamic and responsive to the organization's evolving ecosystem.
By combining these features and functions, DAO governance tokens enable token holders to actively participate in shaping the future of the organization, fostering a decentralized and inclusive decision-making process.
Token Distribution in DAOs:
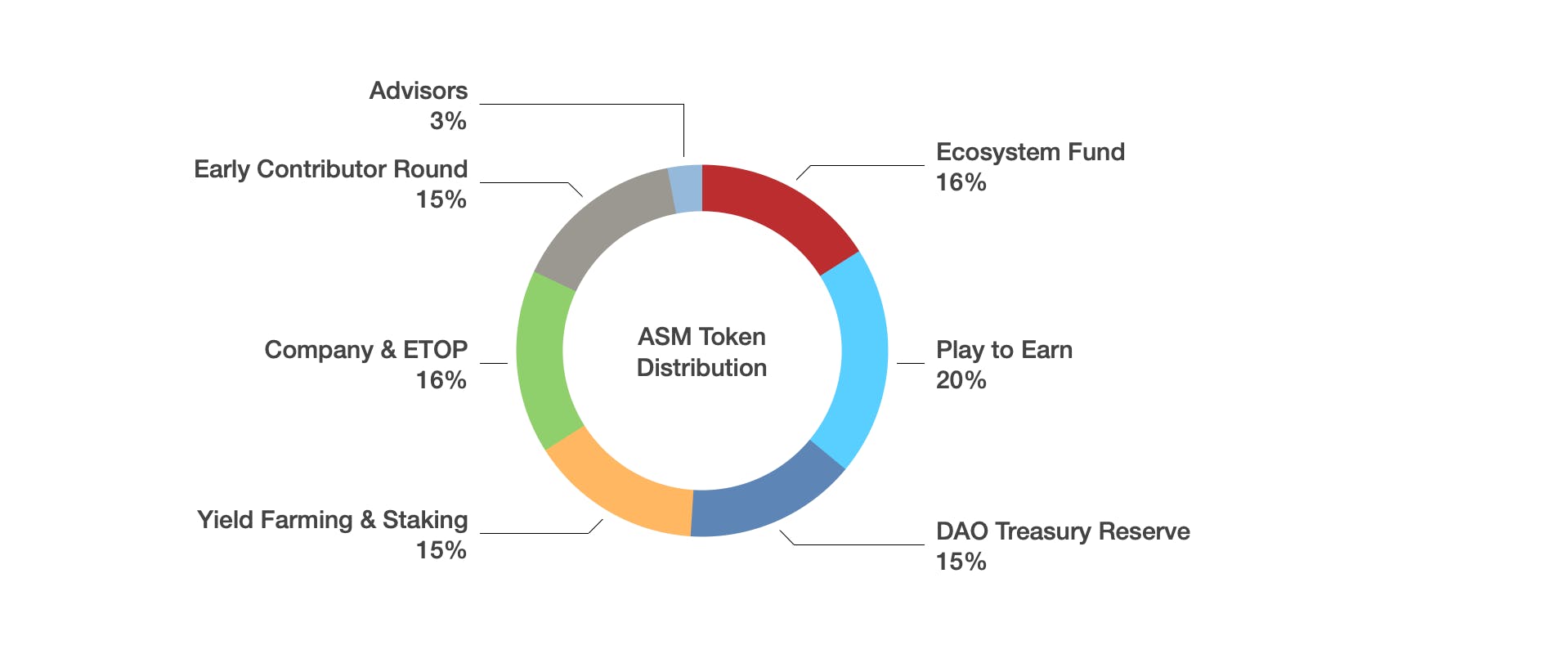
The distribution of DAO governance tokens plays a critical role in establishing a fair and decentralized governance model. The initial allocation of tokens can vary depending on the DAO's design and objectives. Common methods of token distribution include:
Public Sale: DAO governance tokens may be initially offered to the public through a token sale, allowing individuals to acquire tokens in exchange for other cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies. This method aims to distribute tokens widely and attract a diverse community of stakeholders.
Airdrops: Some DAOs opt to distribute a portion of their governance tokens for free through a process called airdropping. Airdrops involve distributing tokens to existing token holders or to individuals who meet certain criteria, such as holding a specific cryptocurrency or participating in specific activities within the ecosystem.
Token Mining: DAOs may implement a token mining mechanism where users can earn governance tokens by contributing resources, such as computing power or liquidity, to the network. Token mining incentivizes participation and contributes to the decentralization of token ownership.
Team and Advisor Allocations: DAO governance tokens are often allocated to the project's founding team, early contributors, and advisors. These allocations can recognize their contributions and align their interests with the long-term success of the organization. However, it is essential to strike a balance between rewarding stakeholders and ensuring a fair distribution to avoid concentration of power.
Initial Governance in DAOs:

Once the tokens are distributed, the DAO needs to establish an initial governance setup to kickstart the decision-making process. Key considerations include:
Governance Framework: DAOs define the rules, processes, and parameters that govern decision-making. This includes establishing voting mechanisms, voting thresholds, and the types of proposals that can be submitted. The governance framework should aim for transparency, inclusivity, and efficiency while addressing potential challenges such as token concentration or malicious attacks.
Proposal Submission and Voting: The DAO sets up a platform or interface where token holders can submit proposals for consideration. The governance tokens are used to cast votes on these proposals. The DAO may decide on the voting duration, quorum requirements, and decision thresholds to determine the outcome of each proposal.
Community Engagement: DAOs often emphasize community engagement and feedback to ensure a vibrant and participatory governance process. Channels such as forums, social media, or dedicated platforms enable token holders to discuss proposals, provide input, and collaborate on decision-making.
Evolutionary Governance: As DAOs grow and mature, it is common for the initial governance setup to evolve based on feedback and community consensus. Upgrades to the governance framework can be proposed and voted upon by the token holders themselves, ensuring the governance mechanisms remain adaptive and responsive to the changing needs of the organization.
By carefully considering token distribution and establishing an initial governance setup, DAOs can foster a decentralized decision-making process that empowers token holders to actively contribute to the organization's future.
Empowering Decentralized Decision Making

Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and their governance tokens have revolutionized decision-making by empowering individuals and communities to actively participate in shaping the future of the organization. Here are several ways in which DAO governance tokens empower decentralized decision-making:
Voting and Proposal Systems
DAO governance tokens grant holders the right to vote on proposals, allowing them to have a direct say in the decision-making process. Token holders can submit proposals themselves or vote on proposals submitted by others. This system ensures that decisions are made collectively, with the voting outcome reflecting the preferences and interests of the token-holder community.
Weighted Voting and Token-Based Influence
DAO governance tokens often employ weighted voting systems where the voting power of each token holder is proportional to the number of tokens they hold. This token-based influence ensures that decisions are not solely based on the number of voters but also take into account the stake and commitment of each token holder. Token-weighted voting promotes a more balanced and representative decision-making process.
Participatory Democracy and Token Holder Engagement
DAO governance tokens promote participatory democracy by encouraging token holders to actively engage in the decision-making process. By holding governance tokens, individuals become stakeholders with a vested interest in the organization's success. This incentivizes token holders to contribute their perspectives, ideas, and expertise, fostering a diverse and collaborative environment for decision-making.
Transparency and Accountability
Decentralized decision-making in DAOs is often accompanied by a high degree of transparency and accountability. Blockchain technology enables the recording and tracking of all governance activities, including voting records and proposal history. This transparency allows token holders to scrutinize the decision-making process, ensuring that it is fair, unbiased, and aligned with the best interests of the DAO and its community.
Furthermore, DAO governance tokens incentivize active participation by aligning the economic interests of token holders with the success of the organization. Token holders can earn additional rewards or benefits through token staking, participating in governance activities, or contributing to the DAO's ecosystem. These incentives encourage token holders to take an active role in decision-making, as their contributions directly impact their financial interests.
By empowering decentralized decision-making, DAO governance tokens unlock the potential for collective intelligence and harness the diverse perspectives of token holders. This democratic and inclusive approach enables DAOs to make informed decisions that reflect the values and goals of their communities. As a result, the decision-making process becomes more resilient, adaptable, and representative, driving the growth and development of decentralized organizations.
Evolution of DAO Governance Tokens

DAO governance tokens have evolved significantly since their inception, incorporating new features and functionalities that enhance their utility and impact. Here are some key aspects of the evolution of DAO governance tokens:
Token Utility and Ecosystem Expansion: Initially, DAO governance tokens primarily represented voting rights and ownership within the organization. However, as DAOs have grown in complexity and functionality, governance tokens have expanded their utility within the ecosystem. For example, governance tokens can now serve as a medium of exchange within the DAO's decentralized applications (dApps) or grant access to specific features, services, or resources within the ecosystem. This expansion of token utility enhances the value proposition of governance tokens and further aligns the interests of token holders with the success of the DAO.
Staking and Yield Generation
To incentivize active participation and provide economic benefits to token holders, DAO governance tokens have integrated staking mechanisms. Token holders can stake their tokens in various protocols, such as liquidity pools or lending platforms, to earn additional rewards or yield. Staking not only incentivizes token holders to actively engage in the governance process but also contributes to the liquidity and growth of the DAO ecosystem.
Delegated Voting and Proxy Systems
Recognizing that not all token holders may have the time, expertise, or desire to actively participate in voting, DAO governance tokens have introduced delegated voting systems. Token holders can delegate their voting rights to trusted individuals or entities, who can then vote on their behalf. Delegation ensures that voting power is effectively utilized and enables specialized expertise or domain knowledge to play a role in the decision-making process. Proxy systems further enhance the delegation process by allowing token holders to assign voting decisions to trusted third-party delegates, increasing flexibility and convenience.
Integrating DAO Governance Tokens with Other DeFi Protocols
DAO governance tokens have also started integrating with other decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. For example, governance tokens can be used as collateral for borrowing and lending, providing liquidity for decentralized exchanges, or participating in yield farming strategies. These integrations create synergies between different DeFi platforms, enabling DAO governance tokens to leverage the broader DeFi ecosystem for increased liquidity, yield generation, and utility.
The continuous evolution of DAO governance tokens is driven by the collective feedback, ideas, and innovation within the DAO community. As DAOs mature and new challenges arise, governance token models are iterated upon, incorporating improvements and enhancements to better serve the needs of the ecosystem and token holders.
The future of DAO governance tokens is likely to witness further advancements, such as increased interoperability between different DAOs, the introduction of advanced voting mechanisms, integration with decentralized identity solutions, and the exploration of novel incentive models. These innovations will continue to strengthen the role of DAO governance tokens in empowering decentralized decision-making and driving the growth and adoption of decentralized organizations.
Use Case Of Dao: Does it work in real life?

Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) have emerged as a versatile and innovative model for various applications across different industries. Here are some notable use cases of DAOs:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
DAOs have found significant traction in the DeFi space, where they facilitate decentralized lending, borrowing, trading, and other financial services. DAOs enable the community to collectively govern protocols, determine lending rates, vote on upgrades, and manage liquidity pools. By leveraging DAO governance tokens, DeFi platforms can achieve transparent and community-driven decision-making, enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of financial services.
Decentralized Governance and Organizations:
One of the primary use cases of DAOs is in decentralized governance and organizational structures. DAOs enable communities to collectively manage and govern resources, make decisions, and distribute rewards transparently and inclusively. These organizations can range from decentralized communities and cooperatives to open-source projects, empowering participants to actively shape the direction and operations of the organization.
Collective Investment and Venture Capital
DAOs have emerged as a model for collective investment and venture capital funding. Participants pool their funds into a DAO and collectively decide on investment opportunities, startup funding, and project support. The decentralized nature of DAOs enables a diverse group of individuals to participate in investment decisions, providing opportunities for early-stage funding and fostering innovation in the startup ecosystem.
Content Creation and Curation
DAOs are being utilized in the realm of content creation and curation. Participants can contribute their skills, knowledge, or creative works to a DAO-managed platform, and the community collectively governs the content quality, distribution, and monetization. DAOs enable fair compensation, ownership rights, and decentralized decision-making in content platforms, empowering creators and curators to have greater control over their work.
Decentralized Marketplaces
DAOs are being leveraged to create decentralized marketplaces that allow participants to trade goods, services, or digital assets without intermediaries. These marketplaces can incorporate DAO governance tokens for decision-making, dispute resolution, and community-driven rule enforcement. By removing central authorities and intermediaries, decentralized marketplaces enable direct peer-to-peer interactions, reducing costs, and promoting trust and transparency.
Decentralized Governance for Cities and Communities
DAOs are being explored as a means to enhance governance in cities and communities. By enabling community members to actively participate in decision-making processes, DAOs can foster more inclusive and transparent governance models. This can include initiatives such as community funds, resource allocation, urban planning, and public service management, allowing citizens to collectively shape the development and governance of their communities.
These are just a few examples of the diverse use cases of DAOs. As the technology continues to evolve, DAOs are likely to find application in other sectors, such as supply chain management, healthcare, education, and social impact initiatives. The decentralized and community-driven nature of DAOs has the potential to revolutionize traditional systems and empower individuals to participate in decision-making and value creation.
Vibrant DAO Communities

DAOs have demonstrated their potential and effectiveness across various industries, revolutionizing the way organizations operate and make decisions. Here are a few notable case studies highlighting successful DAO endeavors:
MakerDAO
MakerDAO is a decentralized credit platform built on the Ethereum blockchain. It operates as a DAO and is responsible for governing the creation and management of the stablecoin DAI. MakerDAO token holders, through their voting power, make critical decisions such as adjusting the stability fees, collateral types, and system parameters. MakerDAO's success lies in its ability to provide decentralized stablecoin issuance, allowing users to leverage their crypto assets without relying on traditional financial institutions.
Aragon
Aragon is a platform that enables the creation and management of decentralized organizations. It provides tools and infrastructure for DAO governance, including voting, fundraising, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Aragon DAOs have been utilized for a variety of purposes, ranging from community-driven projects to decentralized investment funds. Aragon's case study showcases the power of DAOs in providing a robust framework for creating and managing decentralized organizations.
MolochDAO
MolochDAO is a grant-giving DAO focused on funding Ethereum ecosystem projects. It operates on the principles of collective decision-making and aims to provide financial support to initiatives that enhance the Ethereum ecosystem. MolochDAO has successfully funded numerous projects and initiatives, including developer grants, infrastructure improvements, and research initiatives. Its case study exemplifies the effectiveness of DAOs in funding and supporting open-source projects and decentralized ecosystems.
Gitcoin Grants:
Gitcoin Grants is a funding platform that utilizes DAO principles to support open-source projects and public goods in the blockchain space. Through its quadratic funding mechanism, Gitcoin Grants enables individuals to contribute funds to projects, and those funds are matched by sponsors and the community. The decision-making process for allocating funds is decentralized, with token holders voting on the distribution of grants. Gitcoin Grants has successfully facilitated the funding of numerous projects, fostering innovation and collaboration in the blockchain ecosystem.
These case studies demonstrate the successful implementation of DAOs across different domains, including investment, decentralized governance, stablecoin issuance, and funding open-source initiatives. They highlight the potential of DAOs in enabling decentralized decision-making, fostering community participation, and driving innovation. As technology continues to evolve and more organizations embrace the DAO model, we can expect further case studies showcasing the power and impact of DAO endeavors.
Benefits and challenges of DAO:

In the world of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), governance tokens play a pivotal role in empowering decentralized decision-making. They provide individuals and communities with the means to actively participate in shaping the future of the organization. However, alongside these benefits, DAO governance tokens also present unique challenges, including token concentration, Sybil attacks, balancing efficiency and security, and navigating regulatory considerations. Understanding both the benefits and challenges of DAO governance tokens is essential for harnessing their full potential and creating robust and effective decentralized organizations.
Benefits of DAO

a) Decentralized Decision-Making: DAO governance tokens enable decentralized decision-making by granting token holders the ability to vote on proposals and actively participate in shaping the future of the organization. This promotes inclusivity, transparency, and community engagement in governance processes.
b) Token Holder Alignment: By owning governance tokens, individuals become stakeholders with a direct financial interest in the success of the DAO. This alignment incentivizes token holders to act in the best interests of the organization, leading to more thoughtful and informed decision-making.
c) Incentivized Participation: DAO governance tokens provide economic incentives for active participation in governance activities. Token holders can earn additional rewards, yield, or other benefits through staking, voting, or contributing to the ecosystem. These incentives foster a vibrant and engaged community, driving the growth and development of the DAO.
d) Flexibility and Upgradability: DAO governance tokens offer flexibility in governance mechanisms, allowing for the evolution of decision-making processes over time. Upgrades and improvements can be proposed and voted upon by token holders, ensuring that the governance framework remains adaptive and responsive to the changing needs of the organization and its ecosystem.
Challenges of DAO

a) Governance Token Concentration: A challenge inherent to DAO governance tokens is the potential for token concentration in the hands of a few large stakeholders. Concentration of governance power can lead to centralization and reduced inclusivity in decision-making. DAOs must implement measures to address this challenge, such as token redistribution mechanisms or introducing protocols that mitigate the influence of large token holders.
b) Sybil Attacks and Identity Verification: DAO governance tokens face the risk of Sybil attacks, where individuals create multiple identities to gain disproportionate influence over decision-making. Verifying the identity of token holders is crucial to ensure a fair and secure governance process. DAOs need to implement robust identity verification mechanisms or integrate with decentralized identity solutions to mitigate this challenge.
c) Balancing Efficiency and Security: DAO governance tokens must strike a balance between efficiency and security in decision-making. While rapid decision-making is desirable, it is essential to ensure that the governance process incorporates adequate security measures to prevent malicious attacks, vulnerabilities, or manipulation of voting outcomes.
d) Regulatory and Compliance Considerations: DAO governance tokens may encounter regulatory challenges and compliance requirements, as the legal and regulatory frameworks for decentralized organizations continue to evolve. DAOs must navigate these complexities to ensure their governance processes comply with relevant laws and regulations without compromising their decentralized nature.
e) Network Congestion: As DAOs gain popularity and attract a larger user base, the blockchain network on which they operate can become congested. High transaction volumes and limited network capacity may result in slower transaction processing times, increased fees, or even network failures. These limitations can hinder the efficiency and responsiveness of governance processes within DAOs.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research, community engagement, and collaboration within the DAO ecosystem. By actively recognizing and working to overcome these obstacles, DAO governance tokens can continue to enhance decentralized decision-making and foster the growth of decentralized organizations.
Future of DAOs

Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) have emerged as a powerful paradigm for organizing and governing communities in a decentralized manner. As DAOs continue to evolve and gain widespread adoption, the future holds several exciting possibilities for their development and impact. Here are some key areas that indicate the promising future of DAOs:
Mainstream Adoption
The future of DAOs lies in their potential for mainstream adoption. As the technology matures and becomes more user-friendly, DAOs have the opportunity to attract a broader audience beyond the crypto-savvy community. Simplified user interfaces, intuitive governance platforms, and improved onboarding processes will play a crucial role in making DAOs accessible and appealing to a wider range of individuals, including non-technical users.
Interoperability and Collaboration
Interoperability among different DAOs and blockchain networks will be a significant focus in the future. DAOs will strive to collaborate and share resources, allowing for cross-DAO interactions and coordination. Inter-DAO collaborations can unlock new possibilities for pooling resources, conducting joint initiatives, and leveraging each other's strengths, ultimately leading to a more connected and vibrant ecosystem.
Integration with Traditional Systems
The future of DAOs also involves exploring integration with traditional systems and institutions. As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, DAOs will seek ways to comply with legal frameworks while preserving their decentralized nature. Integration with traditional financial systems, legal frameworks, and governance structures can pave the way for DAOs to interact and collaborate with traditional organizations, fostering innovation and creating new avenues for decentralized decision-making.
Enhanced Governance Mechanisms
The governance mechanisms of DAOs will continue to evolve and improve. Experimentation with different voting models, consensus algorithms, and decision-making frameworks will lead to more efficient, inclusive, and secure governance processes. Additionally, advances in decentralized identity solutions and reputation systems will enable DAOs to establish trust and ensure the credibility of participants, further enhancing the effectiveness of governance mechanisms.
Tokenization and Token Standards
Tokenization will play a pivotal role in the future of DAOs. The development of token standards, such as ERC-20 and ERC-721, has enabled the creation of fungible and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that represent ownership, voting rights, or access to specific services within a DAO ecosystem. Continued innovation in token standards and the emergence of new tokenization models will unlock diverse use cases, enhance token utility, and create new economic ecosystems within DAOs.
Social and Impact-driven DAOs
In the future, we can expect to see an increase in social and impact-driven DAOs. These DAOs will focus on addressing global challenges, promoting sustainability, and supporting social causes. Through decentralized decision-making and collaborative efforts, social DAOs can mobilize resources, drive positive change, and empower communities to work towards common goals, fostering a more equitable and sustainable future.
The future of DAOs is full of promise and potential. As technology advances, regulatory frameworks evolve, and user adoption grows, DAOs will continue to reshape traditional governance structures, empower individuals, and foster decentralized decision-making. The journey ahead involves overcoming challenges, embracing innovation, and harnessing the collective intelligence and creativity of global communities, leading to a more inclusive, transparent, and collaborative future facilitated by DAOs.

